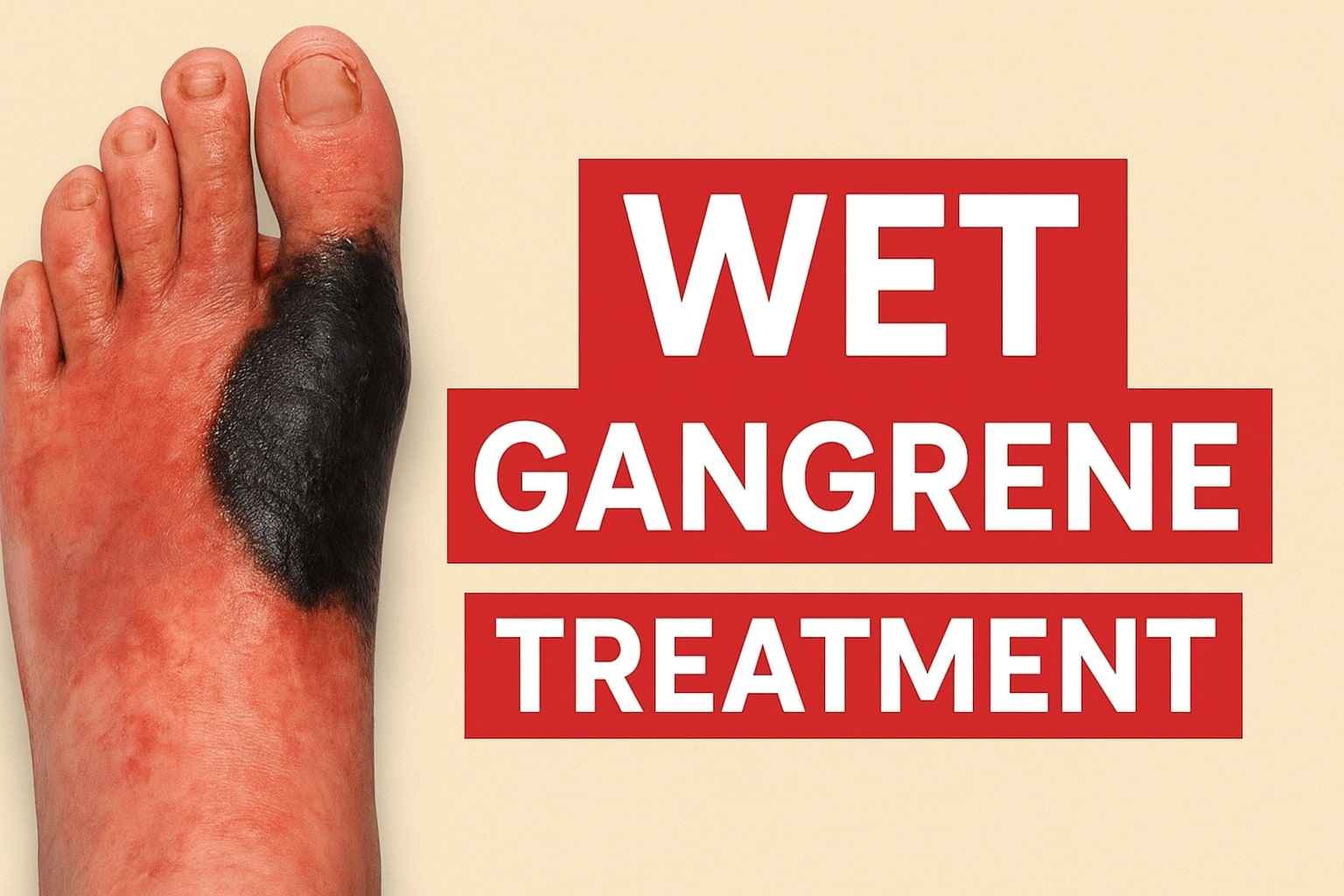
Wet gangrene is a severe, fast-spreading infection of dead tissue caused by poor blood supply and bacterial invasion. Unlike dry gangrene, which develops slowly, wet gangrene can turn a minor wound into a life-threatening emergency within hours or days. Rapid tissue death, foul-smelling discharge, and the high risk of sepsis make immediate medical care essential.
If you are looking for wet gangrene treatment in Gurgaon, understanding the condition and your treatment options can help you act quickly. In this blog, you’ll learn what wet gangrene is, its causes and symptoms, how doctors treat it (including antibiotics and surgery), and how to find the best specialists locally.
What Is Wet Gangrene?
Wet gangrene occurs when a part of the body loses blood supply and becomes infected with bacteria. This infection differentiates wet gangrene from dry gangrene and makes it far more dangerous. Tissues most commonly affected are the feet, toes, hands, and sometimes internal organs.
Key points:
• Caused by tissue death plus bacterial infection
• Spreads rapidly and can lead to sepsis
• Requires emergency hospital care
Causes of Wet Gangrene
Wet gangrene develops because of a combination of poor circulation and infection. Certain health conditions and lifestyle factors increase the risk dramatically. Knowing the causes helps in both prevention and early detection.
Main causes include:
• Diabetes & diabetic foot ulcers – high blood sugar damages vessels and nerves, leading to poor circulation and unnoticed wounds.
• Peripheral artery disease (PAD) – narrowed arteries starve tissues of oxygen and nutrients, making them vulnerable to infection.
• Severe injuries or trauma – burns, frostbite, or crush injuries compromise blood flow and provide an entry point for bacteria.
• Untreated or infected wounds – minor cuts or sores can progress to major infections when not properly cared for.
• Compromised immunity – conditions like cancer, HIV, steroid therapy, or old age lower the body’s defense against infection.
• Lifestyle factors – smoking, high cholesterol, and poor nutrition slow healing and increase gangrene risk.
Symptoms That Require Emergency Care
Recognizing the signs of wet gangrene early can mean the difference between saving and losing a limb. Because the tissue is already dead or dying, the infection spreads quickly and can enter the bloodstream.
Watch for these warning signs:
• Severe pain and swelling around a wound or affected area
• Skin discoloration turning black, green, purple, or bronze
• Foul-smelling discharge or pus indicating bacterial activity
• Thin, shiny, or blistered skin that may feel cool to the touch
• Fever, chills, and rapid heart rate suggesting systemic infection
• Numbness following intense pain – a sign of nerve destruction
How Doctors Diagnose Wet Gangrene
Before treatment begins, doctors must assess the extent of infection and circulatory status. In Gurgaon, most tertiary hospitals follow a similar diagnostic pathway.
Common diagnostic steps:
• Physical exam to check tissue color, pulses, and spread of infection
• Blood tests for infection markers (CRP, ESR, WBC count)
• Imaging such as Doppler ultrasound, CT angiography, or MRI to assess blood flow and tissue damage
• Wound cultures or tissue biopsies to identify bacteria
Wet Gangrene Treatment: Step by Step
Treating wet gangrene requires a multidisciplinary approach to control infection, remove dead tissue, restore blood flow, and support healing.
Emergency Hospital Care
Patients with wet gangrene are admitted immediately. Stabilization, IV fluids, pain control, and fast surgical evaluation happen at once to prevent sepsis and tissue loss.
Antibiotics for Wet Gangrene
Because infection drives wet gangrene, antibiotics are the first line of treatment. Doctors start broad-spectrum IV antibiotics to cover multiple bacteria types.
Typical antibiotic approaches:
• Vancomycin or linezolid combined with piperacillin–tazobactam or a carbapenem
• Ampicillin-sulbactam + clindamycin/gentamicin in polymicrobial infections
• Penicillin + clindamycin for clostridial (gas gangrene) cases
Once lab results come back, the antibiotics are tailored to target the specific bacteria. In most cases, antibiotics continue for 1–3 weeks depending on severity.
Key takeaway: Antibiotics control infection but cannot remove dead tissue. Surgery is almost always required alongside antibiotics.
Surgical Debridement and Amputation
The cornerstone of wet gangrene treatment is surgical removal of all dead and infected tissue
Surgical steps may include:
• Debridement – removing only the infected parts while saving healthy tissue
• Repeated procedures – often more than one surgery is necessary
• Skin grafting – for large wounds after debridement
• Amputation – if infection has spread too far, partial or complete amputation may be necessary to save life
The sooner surgery is done, the higher the chance of saving the limb.
Restoring Blood Flow
If poor circulation caused the gangrene, doctors work to restore blood flow to support healing and prevent future episodes.
Options for restoring circulation:
• Angioplasty – widening blocked arteries with a balloon
• Stenting – inserting a small tube to keep the artery open
• Bypass surgery – rerouting blood flow around blockages
Restored circulation improves healing and prevents future gangrene.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
Some hospitals in Gurgaon offer HBOT as an adjunct treatment. Patients breathe pure oxygen in a pressurized chamber, which:
Benefits of HBOT:
• Increases oxygen in tissues
• Inhibits bacterial growth
• Speeds wound healing
HBOT is not a substitute for surgery but can be helpful in difficult cases.
Supportive Care & Lifestyle Management
Recovery doesn’t end after surgery. Patients must address underlying risk factors to avoid recurrence.
Supportive measures include:
• Eating a high-protein diet for tissue repair
• Taking Vitamin C and zinc to aid wound healing
• Keeping wounds clean and covered under medical supervision
• Managing diabetes, blood pressure, and cholesterol
• Quitting smoking to improve circulation
Wet Gangrene Treatment in Gurgaon
Gurgaon (Gurugram) is home to some of India’s top hospitals and vascular surgery units. If you’re searching for “Wet Gangrene Treatment in Gurgaon”, look for facilities with advanced care.
What to look for in a hospital:
• Vascular surgery and ICU facilities
• Infectious disease specialists for tailored antibiotic therapy
• Access to angioplasty, bypass, and HBOT
• Multidisciplinary wound care teams
Recommended Hospitals & Specialists
• Medanta – The Medicity, Gurugram: Offers comprehensive diabetic foot and gangrene management with vascular surgery, infectious disease, and wound care units.
• Paras Hospitals, Gurgaon: Known for vascular surgery and limb salvage procedures.
• Leading vascular surgeons in Gurgaon: Search online directories for specialists experienced in diabetic foot and gangrene.
Questions to Ask Before Choosing a Doctor
• How many wet gangrene cases have you treated?
• Do you offer 24/7 surgical and ICU support?
• Is HBOT or advanced wound care available onsite?
• What is your limb salvage rate?
Preventing Wet Gangrene
Prevention is far easier than treatment, especially if you’re in a high-risk group.
Prevention tips:
• Strictly control blood sugar, cholesterol, and blood pressure
• Promptly treat small wounds or ulcers
• Wear protective, comfortable footwear
• Quit smoking to maintain circulation
• Schedule regular vascular check-ups if you have PAD or diabetes
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Recognizing common questions helps address readers’ concerns and can win you rich snippets in Google search.
Q: Can wet gangrene be cured without surgery?
A: Early cases may respond to aggressive antibiotics plus minor debridement, but most require some form of surgical removal of dead tissue.
Q: How long do antibiotics for wet gangrene last?
A: Typically 1–3 weeks, but longer if bone or deep tissue infection persists.
Q: Is hyperbaric oxygen therapy necessary?
A: Not always, but it can help in stubborn or extensive wounds. Surgery remains primary.
Q: How much does wet gangrene treatment cost in Gurgaon?
A: Costs vary by hospital, procedures, and length of stay. Government hospitals may be more affordable, while private hospitals offer advanced options at higher costs.
Q: Which doctor should I see for wet gangrene?
A: Start with emergency care. A vascular surgeon and an infectious disease specialist are usually part of the core treatment team.
Conclusion
Wet gangrene is a serious, fast-spreading infection of dead tissue that can lead to sepsis, amputation, or death if not treated immediately. Prompt hospital care, IV antibiotics, surgical debridement, and restoration of blood flow are critical. If you’re in Gurgaon and suspect wet gangrene, go to a hospital with vascular surgery, wound care, and infectious disease specialists. Early action can save both life and limb. After treatment, maintaining mobility and proper support is crucial for recovery. Check out Mobility Solution for reliable mobility aids and rehabilitation services to help patients regain strength and move safely post-treatment.